
Top 5 Challenges in Building ASR Models (and How High-Quality Data Solves Them)
This article breaks down the top-five challenges in building ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) models and shows how high-quality, ethically sourced data can help solve them. You’ll learn why language diversity, domain-specific vocabulary, audio quality, data annotation and ethical AI matter, and how they can help to future-proof your ASR model strategy.
TL;DR
Core ASR Challenges and Solutions
From language diversity and domain-specific vocabulary to audio quality and annotation accuracy, curated datasets are the recommended option to fine-tune ASR performance.
Data Quality as a Differentiator
High-quality, well-annotated and diverse audio data is the foundation for low Word Error Rate (WER) and robust ASR models.
Ethical AI and Compliance
Data provenance, consent for use in AI training and regulatory alignment are critical for user trust, global compliance and scalability.
Future Trends in ASR
Emerging technologies like agentic voice AI, speech-to-speech models, advanced real-time inference optimization and synthetic training data are what to look out for.
Introduction: Why ASR Is Harder Than It Sounds
ASR, which encompasses speech-to-text (STT), is no longer a niche technology. In fact, it’s all around us, powering healthcare transcription, automotive voice assistants, call center automation and even GenAI experiences. An ASR model’s job is to transcribe audio commands and queries into text that can then be combined with other AI technologies like intent recognition or emotion detection to build accurate, flowing conversations. If the model is poorly trained, customers are left pleading with unhelpful and confused AI agents rerouting them through dystopia.
So, if ASR models are everywhere, they must be easy to build—right?
On paper, it seems simple: feed a model tons of audio data and let machine learning do its magic. However, the reality is far more complex. Even modern ASR models, which combine tasks through deep learning and neural networks, can also integrate complementary technologies and approaches like large language models (LLMs) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). Let’s take a high-level look at the process:
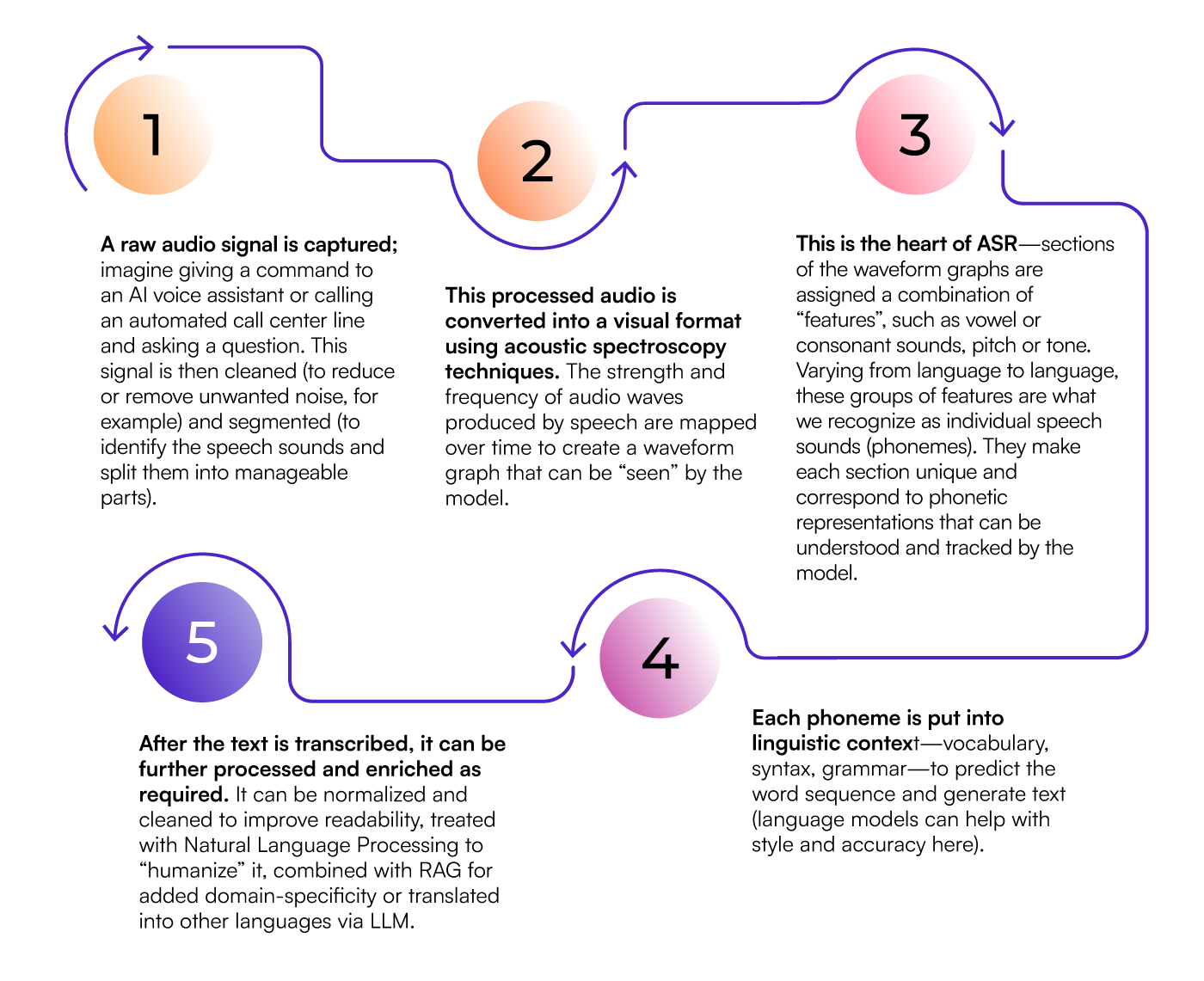
Data and ASR
When it comes to data, foundation models need a lot of unlabeled data to get started, but world-class ASR performance hinges on keeping that WER to a minimum. This demands high-quality, well-annotated ethically sourced data that reflects real-world audio conditions and contexts, as well as continuous model evaluation.
Challenge 1: Language Coverage and Accent Variability
Problem:
ASR models often fail when trained on insufficient language data. For niche or low-resource languages, the lack of diverse speech samples covering different dialects, speaking styles and contexts creates blind spots. Even when the base language is covered, variations can derail performance: a model trained on US English may not have the data to correctly understand different accents within the same language.
Why It Matters:
Healthcare providers in multilingual regions or automotive companies, for example, require diverse models that understand regional languages and dialects. Doctors need to know what patients are telling them make accurate diagnoses, and patients need to understand what they're being told to make informed decisions; a car still drives the same when you cross a border, but drivers can speak any language. In call centers serving global customers, misinterpretation can lead to poor customer experience and operational inefficiencies.
Solution:
- Collect large volumes of speech data in the target language, including conversational and spontaneous speech, especially when building foundation models.
- Use custom data collection platforms, Iike Neevo, to source rare language samples and accent variations.
- Remove bias by balancing representation across dialects and accents.
Challenge 2: Domain-Specific Vocabulary
Problem:
Generic ASR models stumble on technical jargon, so words may be confused, mixed up or misunderstood altogether. For users to trust voice AI, systems need to be able to use the right words in the right context just like a human expert would.
Why It Matters:
In healthcare, misinterpreting “angioplasty” could have serious consequences for patient outcomes. In the automotive industry, failing to recognize “torque converter” impacts voice assistant usability.
Solution:
- Incorporate domain-specific speech data during training.
- Annotate datasets with context-aware transcriptions to capture specialized vocabulary, names of people and places or foreign and loan words.
- Choose professionally recorded datasets for clarity and consistency.
Challenge 3: Audio Quality and Background Noise
Problem:
Real-world audio is messy: think call center recordings with background chatter or telephony data with poor reception. ASR models that need to adapt to different audio contexts trained on clean data alone often fail in noisy environments, leading to high WER.
Why It Matters:
By default, call centers and telephony systems operate in non-ideal audio environments, so they have to deal with whatever is on the other end of the line to provide good customer service. Automotive voice assistants must handle road and traffic sounds, passenger conversations and other audio sources like the radio (or noisy children!) to interpret the driver’s commands. Healthcare recordings, like doctor-patient conversations where accuracy is paramount, could be captured on low-quality microphones or include distracting ambient sounds.
Solution:
- Augment training with low-quality audio samples, like real-world call center recordings, to improve model resilience.
- Invest in custom recordings from professional studios for baseline quality.
- Apply Voice Activity Detection (VAD) during annotation to separate human vocalizations from other sound sources.
Challenge 4: Annotation Quality and Time-to-Market
Problem:
Annotation is labor-intensive. Many open-source datasets lack consistent labeling, slowing time-to-market and compromising accuracy (not to mention potentially introducing bias and regulatory compliance issues).
Why It Matters:
For the best ASR performance, fine-tuning almost always requires audio paired with accurate transcripts. Poor annotation means higher WER and longer development cycles.
Solution:
- Use expert linguists and QA processes to ensure annotation quality.
- Consider text transcription services and custom annotation pipelines to accelerate deployment.
- Implement context-aware labeling for domain-specific applications.
Challenge 5: Data Scarcity for Specialized Use Cases
Problem:
Data required for niche applications is often limited, if it exists at all. And even with all the data society produces, the pace that AI uses it up for training means we’ll need to consider alternative ways of generating it in the short to medium term.
Why It Matters:
Healthcare voice assistants need medical dialogue. Automotive systems need in-car conversational data. Call centers need multilingual, noisy recordings. Whatever the industry or use case, data of all shapes, types and sizes underpins AI solutions.
Solution:
- Conduct custom collections through crowd platforms.
- Use synthetic data generation via text-to-speech (TTS) to augment datasets.
- Leverage recording studios for high-quality, domain-specific audio.
Bonus Challenge: Ethical AI, Data Privacy and Provenance
Problem:
Many open-source audio datasets (LibriSpeech, Common Voice, GigaSpeech) lack specific consent for AI training, have inconsistent annotations or are not copyright cleared. Regulatory scrutiny is increasing, so ethical sourcing is not only good practice but also a competitive advantage.
Why It Matters:
The healthcare and automotive industries operate under strict compliance frameworks like HIPAA and the EU AI Act, UNECE and GDPR. Using non-consented data exposes companies to legal, brand and reputational risks.
Solution:
- Source 100%-consented, ethically collected data.
- Maintain audit trails for data provenance.
- Align with global AI regulations and emerging standards for responsible AI.
- Communicate ethical practices to customers: trust drives adoption.
How Defined.ai’s High-Quality AI Data and Services Can Help
- Volume and Diversity: Our large, curated datasets reduce WER and improve generalization. In fact, with more than 2.5 million hours of speech data available (and counting), we have the world's biggest collection of ethically sourced AI-ready datsets for ASR!
- Annotation Accuracy: ASR model fine-tuning requires precise audio transcripts, speaker segmentation, conversational speech handling and more. Whatever your model needs, our expert-led, human-in-the-loop workflows guarantee quality and speed.
- Domain and Language Coverage: As the world’s largest data marketplace for AI solutions, we offer specialized datasets for healthcare, automotive, call centers and more in over 500 languages and dialects.
- Noise Handling: With our professionally equipped in-house recording studio producing world-class audio for baseline quality and datasets with varied sonic environments, train your ASR model for real-world adaptability.
- Ethical Compliance: Every dataset is sourced with specific consent for AI training, full copyright clearance and globally recognized data privacy and security compliance.
Future Trends: What’s Next for ASR?
If there’s one thing about AI that everyone knows, it’s that it rarely stands still. So, while it’s important to be up-to-date, it also pays to think ahead and plan your long-term AI strategy. But remember, whatever the next big thing in ASR might be, high-quality, ethically sourced data will never go out of fashion!
Agentic AI Voice Solutions
Voice assistants are evolving into agentic AI systems capable of autonomous decision-making. This will require richer datasets providing prosody and emotional nuance, so AI models understand the subtleties behind commands and requests and respond more naturally; not just words, but tone, intent and sentiment.
Speech-to-Speech Models
The current ASR model stack—STT + LLM + TTS—is stable but can be improved. Emerging speech-native models promise direct speech-to-speech interaction. ASR will become part of a unified pipeline, requiring real-time inference optimization and VAD.
Synthetic Data and Data Augmentation
The internet is running out of real-world data. Synthetic audio generated via existing real-world data or TTS could fill the gap, increasing volume and diversity. We might even see hybrid datasets combining real and synthetic speech.
Regulation and Responsible AI
AI laws and regulation with global reach will become more refined and might be the default rather than a choice. Ethical sourcing and data provenance will become non-negotiable for customers, with laggard brands paying with their reputations and potential costly law suits.
Conclusion: Data Is the Foundation of ASR Success
Building ASR models isn’t just about algorithms, it’s also about data. From language diversity and domain-specific vocabulary to varied audio conditions and ethical compliance, the challenges are real but solvable. High-quality, annotated and ethically sourced datasets are the foundation for ASR systems that perform accurately and reliably in any industry and environment.
Ready to build ASR models that work in the real world? Explore the world’s largest on-demand Data Marketplace or contact us to discuss custom data collection and annotation.
Speak to an ASR expert.
Fill in the form below and we'll be in touch soon!